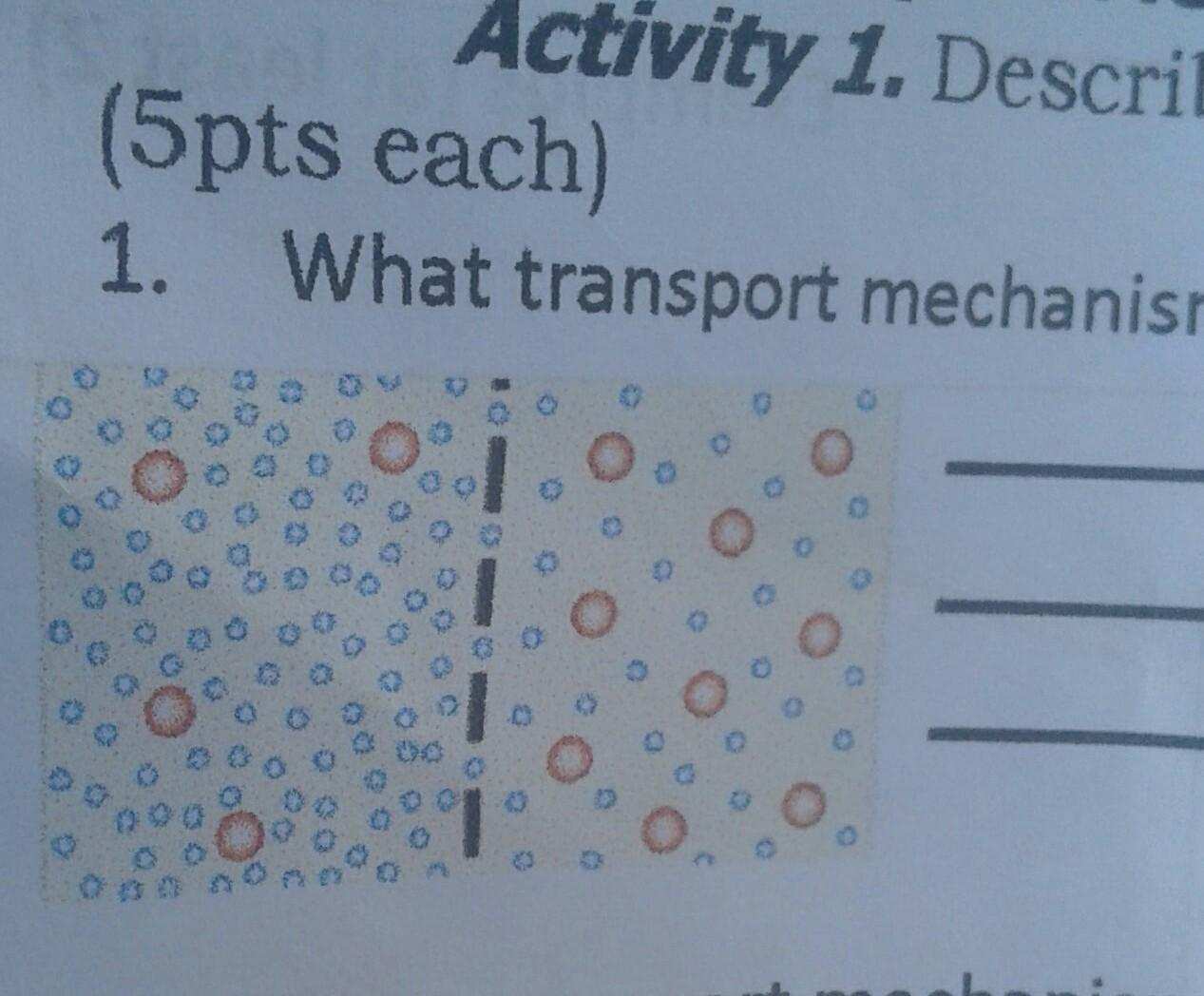
what transport mechanism will the red molecules exhibit?
Answers 1
Answer:
In cellular biology, membrane transport refers to the collection of mechanisms that regulate the passage of solutes such as ions and small molecules through biological membranes, which are lipid bilayers that contain proteins embedded in them.
There are three main types of passive transport:
Simple diffusion – movement of small or lipophilic molecules (e.g. O2, CO2, etc.)
Osmosis – movement of water molecules (dependent on solute concentrations)
Facilitated diffusion – movement of large or charged molecules via membrane proteins (e.g. ions, sucrose, etc.)
-
Author:
alexhernandez
-
Rate an answer:
4
Do you know the answer? Add it here!
Choose a language and a region
How much to ban the user?
1 hour
1 day
100 years
